Search the Community
Showing results for tags 'cpu'.
-
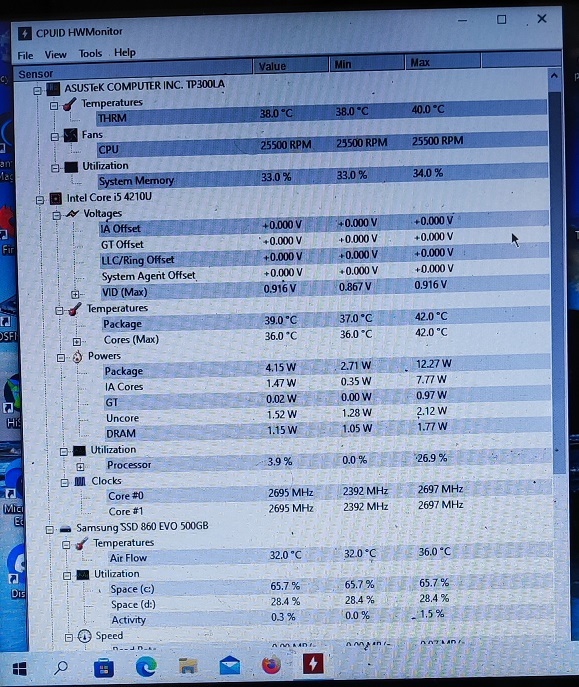
La un laptop Asus TP 300 la care a inceput sa stea ventilatorul procesorului la turatie maxima, desi temperatura CPU este 36-40 de grade. Am curatat coolerul si am schimbat pasta procesorului si nu este nici o diferenta. Am suspectat windows-ul dar la aceiasi turatie sta si cand butez cu un stick in Hiren sau in bios. S-a mai intamplat odata sau de 2 ori cand am repornit sa porneasca la turatie normala. Am facut si update de bios si tot degeaba. Poate fi din alta cauza? Ce mai pot face ca sa depistez cauza?
-
Salut, Am un procesor i5 8400, placa de baza MSI B360 Gaming Plus, 8GB RAM si un CPU cooler CM Hyper 212 Evo. Am aplicat pasta termoconductoare, ca in imaginea din link-ul de mai jos. Temperaturile sunt de maxim 63C in timpul rularii Intel burn test la Stress Level: High. Am decis sa intind pasta pe CPU din cauza ca mai demult am folosit metoda bobului de orez si atunci nu am reusit sa pozitionez coolerul perfect paralel cu procesorul iar pasta s-a intins doar pe o parte a procesorului. Pasta folosita este MX4. Imagine: https://imgur.com/a/0LXL9fi Zonele de la marginea procesorului, pe care nu a fost aplicata pasta (vedeti imaginea), au fost acoperite cu pasta termoconductoare atunci cand am asezat coolerul pe procesor ? Multumesc anticipat.
-
- cpu
- motherboard
-
(and 1 more)
Tagged with:
-
I'm sure you're asking yourself what exactly is Overclocking and why is it so used , along with Underclocking , an other well known procces in the domain . Well , my opinion is not that important so I will explain what both of them really are . Overclocking is the process of making a computer or component operate faster than the clock frequency specified by the manufacturer by modifying system parameters (hence the name "overclocking"). Operating voltages may also be changed (increased), which can increase the speed at which operation remains stable. Most overclocking techniques increase power consumption, generating more heat, which must be dispersed if the chip is to remain operational The purpose of overclocking is to increase the operating speed of given hardware. The trade-offs are an increase in power consumption and fan noise, the system can become unstable if the equipment is overclocked too much, and the risk of damage due to excessive overvoltage or heat generation. In extreme cases, costly and complex cooling (e.g.,water-cooling) is required. Conversely, underclocking trades off slower operation to reduce power consumption and temperature, cooling requirements (and therefore the number and speed of fans, allowing quiet operation) and, where relevant, increase battery life per charge. Some manufacturers underclock components of battery-powered equipment to improve battery life or implement systems that reduce the frequency when operating under battery. On a large number of newer Intel CPUs (those without unlocked multipliers), because of the CPU's drastic redesign (that is, the replacement of the FSB with the base clock), overclocking - if even possible - comes with high risk of system instability. Undervolting is possible to some extent (depending on motherboard design and CPU quality) and may allow a user to turn a standard voltage CPU into a low voltage CPU without having to pay more, and not be restricted by low voltage CPU's low multiplier. The speed gained by overclocking depends largely upon the application; benchmarks for different purposes are published. Many people overclock their hardware to improve its performance. This is practiced more by enthusiasts than professional users seeking an increase in the performance of their computers, as overclocking carries risks of less reliable functioning and damage. There are several purposes for overclocking. Overclocking allows testing over-the-horizon technologies that available component specifications are not capable of, without having to enter the expensive realm of specialized computing. For professional users, overclocking improves professional personal computing capacity, therefore allowing improved productivity. Hobbyists may enjoy building, tuning, and comparison racing their systems with standardized benchmark software. Some hobbyists purchase less expensive computer components and overclock to higher clock rates in an attempt to save money but achieve the same performance. A similar but slightly different approach to cost saving is overclocking outdated components to keep pace with new system requirements, rather than purchasing new hardware. If the overclocking stresses equipment to the point of failure, little is lost as it is fully depreciated, and would have needed to be replaced in any case. Computer components that may be overclocked include processors (CPU), video cards, motherboard chipsets, and RAM. Most modern CPUs increase their effective operating speeds by multiplying the system clock frequency by a factor (the CPU multiplier). CPUs can be overclocked by manipulating the CPU multiplier, and the CPU and other components can be overclocked by increasing the speed of the system clock (external clock) or other clocks (such as a front-side bus (FSB) clock). As clock speeds are increased components will ultimately stop operating reliably, or fail permanently, even if voltages are increased to maximum safe levels. The maximum speed is determined by overclocking beyond the point of instability, then accepting a slightly lower setting. Components are guaranteed to operate correctly up to their rated values; beyond there different samples may have different overclocking potential. CPU multipliers, bus dividers, voltages, thermal loads, cooling techniques and several other factors such as individual semiconductor clock and thermal tolerances can affect the speed, stability, and safe operation of the computer. via: WikiPedia Those two have their advantages and consequences [ in my opinion ] : OVERCLOCKING : Advantages - Faster clock speed - > Better performance . Disadvantages - Overheating , Lower health of the component . UNDERCLOCKING : Advantages - A more stable system . Disadvantages - Lower clock speed -> Lower performance .
-
Existenta familiei procesoarelor x86 a inceput in anii 1978 cu Intel 8086, ulterior acestea fiind imbunatatite (80186, 80286), dupa care in 1980 Intel a lansat Intel 386 (i386). Acesta a fost urmat de "486 (i486)", de "Pentium (i586)", "Pentium 3/4 (i686)" si de "AMD Athlon/Duron/T-bird (precum i686)". Cum toate procesoarele au avut ca baza aceeasi arhitectura, si numele lor a continut "86", toata familia fiind denumita "x86" (toate fiind pe 32 biti). Asadar, cand auziti x86 inseamna ca procesorul este conceput pe 32 de biti. Procesoarele au evoluat si au aparut cele pe 64 de biti, adica x86 pe 64 de biti, fiind cunoscute sub pseudonimul de x64 (asadar cand auziti x64 inseamna ca procesorul a fost conceput pe 64 de biti). Procesoarele de la Alpha (DEC) si cele de la Motorola (PPC) au fost pe 64 de biti, pana la aparitia procesoarelor de la Intel (Itanium si Xeon) respectiv AmdAthlon64. Diferenta dintre Itanium si PPC versus Athlon64 este aceea ca au complet diferite arhitecturi (comunica diferit prin 1 si 0), Athlon64 comunica la fel precum cele pe 32 biti, dar adauga 64 biti de registrii. De aici numele Athlon64 este "x86-64". Mai multa documentatie: x86 Wikipedia si x86-64 Wikipedia P.S: Vedeti si:
-
In cazul in care doriti sa verificati/aflati temperatura componentelor calculatorului dumneavoastra ei bine, va prezint mai jos cateva programe utile pentru acest lucru: CPU ID Hardware Monitor: http://www.cpuid.com/softwares/hwmonitor.html Hardware Monitor: http://www.hmonitor.com/ Speedfan: http://www.almico.com/sfdownload.php Everest: http://www.lavalys.com/support/downloads Real Temp: http://www.techpowerup.com/realtemp/ SiSoftSandra: http://www.softpedia.com/get/System/System-Info/SiSoftware-Sandra.shtml GPU-Z (doar pentru placa video): http://www.techpowerup.com/downloads/1864/mirrors.php HDD Temp (doar pentru hard disk): http://hddtemp.com/ Abyssal Temp Monitor (doar pentru hard disk si procesor ): http://www.abyssalsoft.com/ro/products/abyssal-temp-monitor/ Exemplu: Numai bine !
- 2 replies
-
- temperatura
- cpu
-
(and 3 more)
Tagged with: